Extending ggplot2
with custom Geoms and Stats
James Otto
Introduction
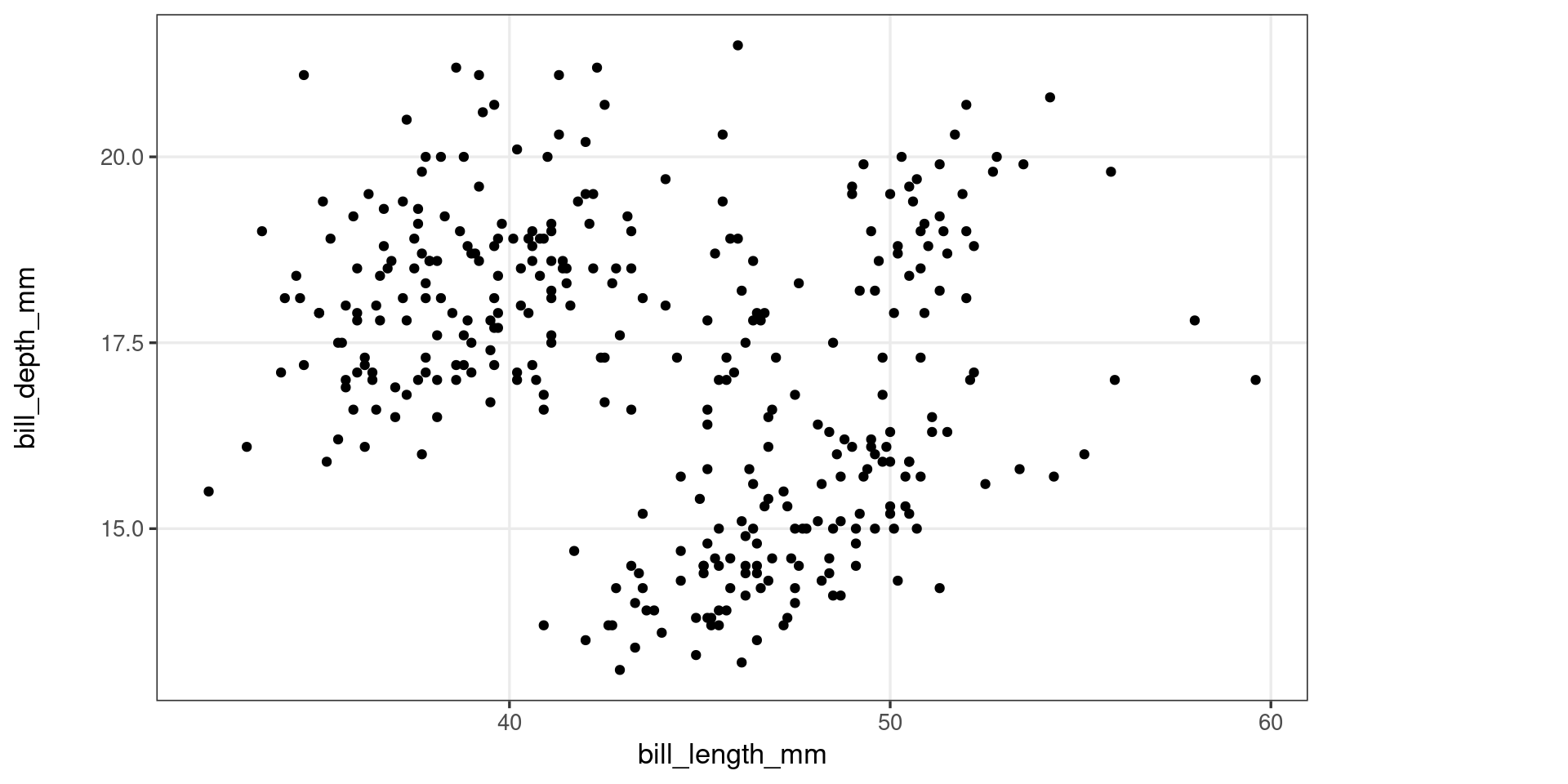

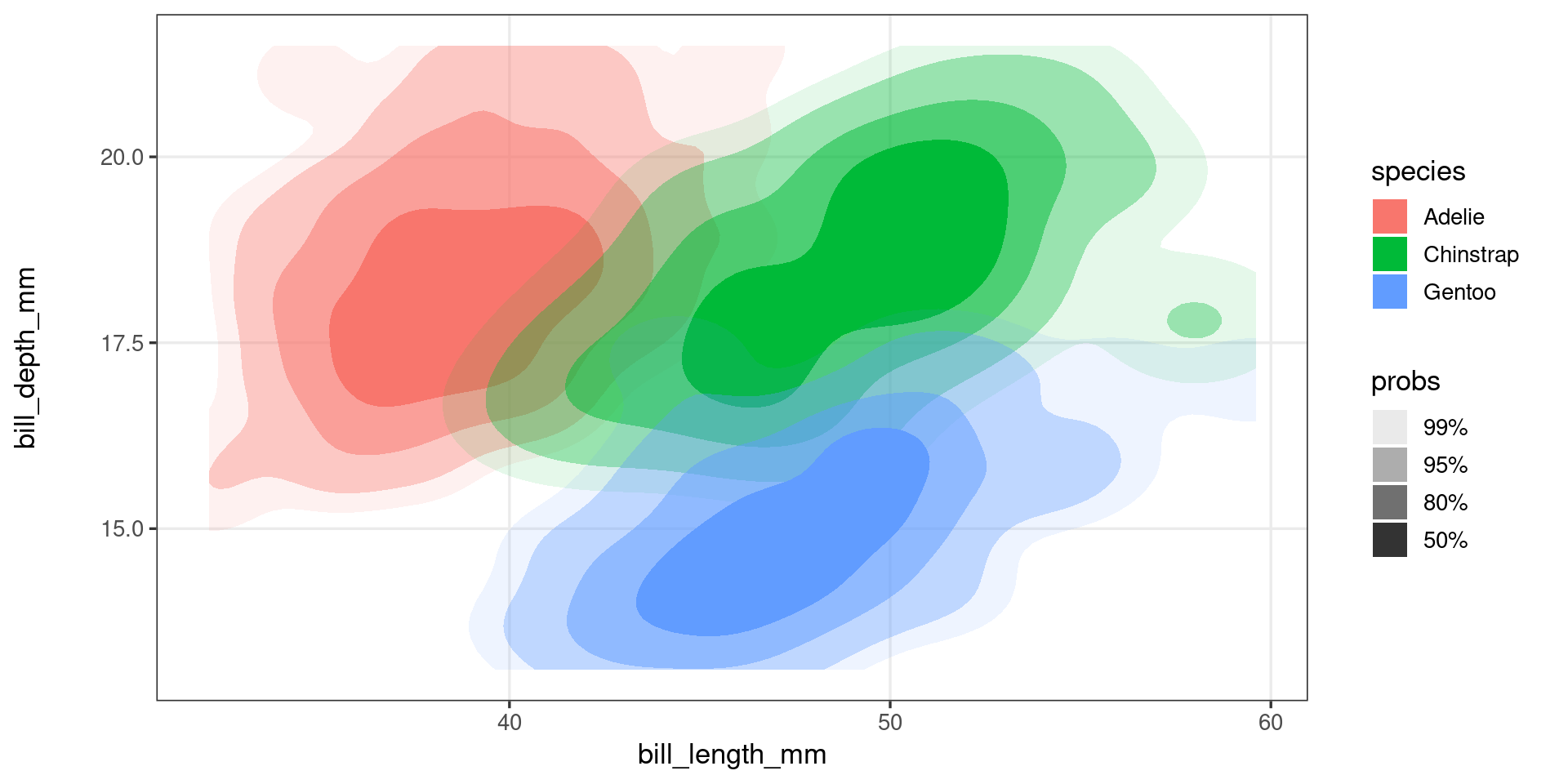
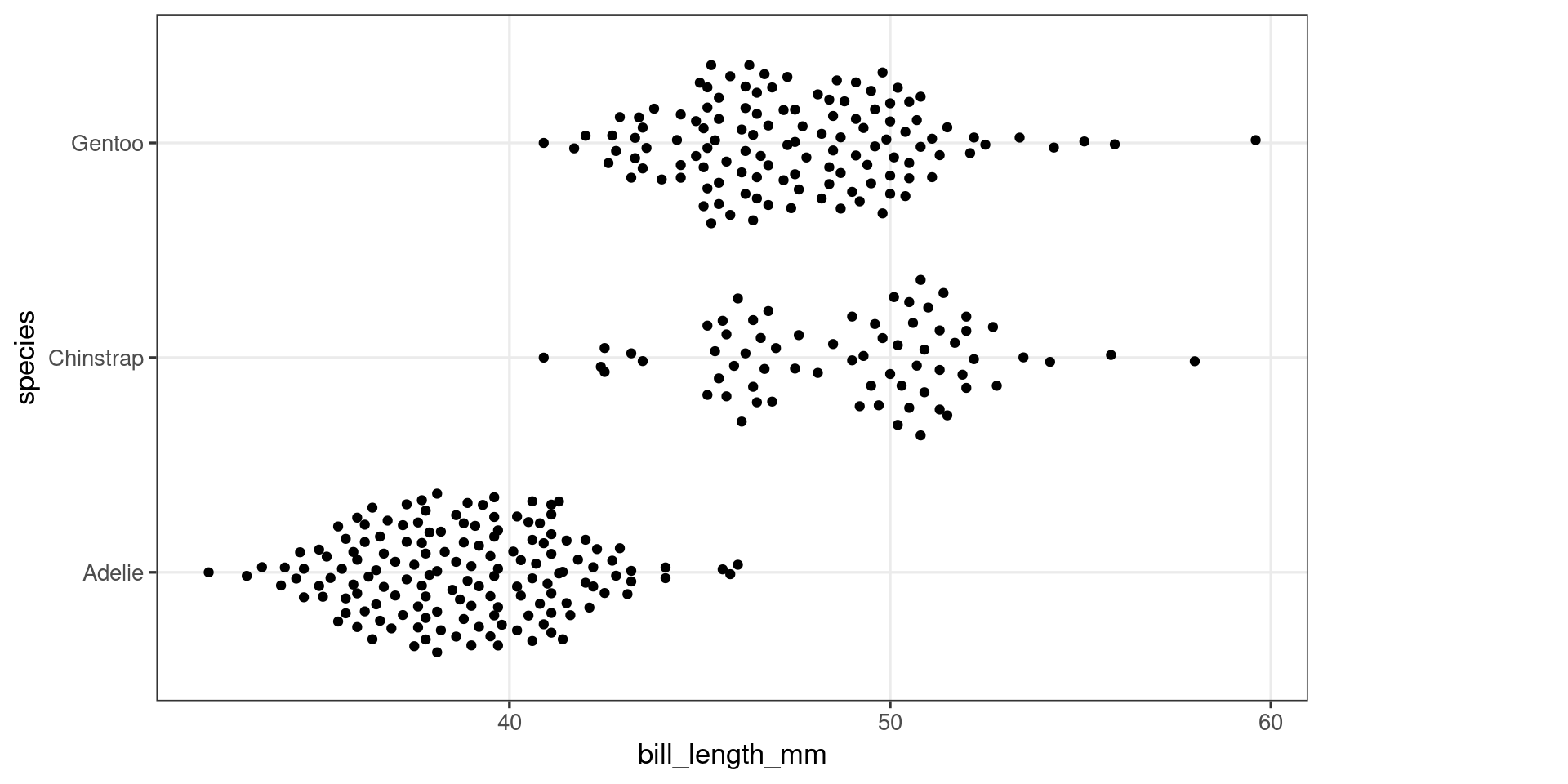
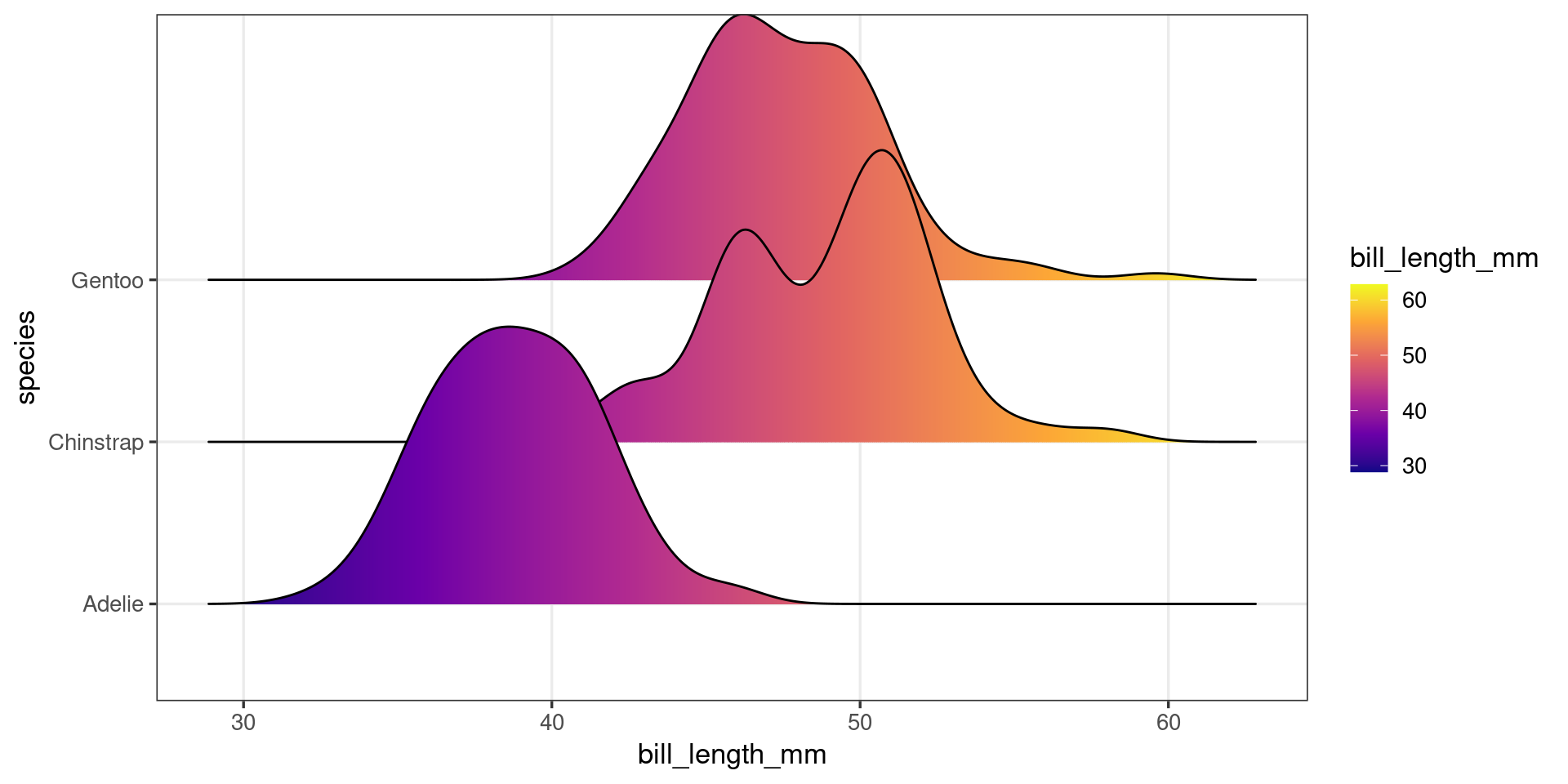
A first look at ggproto objects

function (mapping = NULL, data = NULL, stat = "identity", position = "identity",
..., na.rm = FALSE, show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE)
{
layer(data = data, mapping = mapping, stat = stat, geom = GeomPoint,
position = position, show.legend = show.legend, inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list2(na.rm = na.rm, ...))
}
<bytecode: 0x559a5e930678>
<environment: namespace:ggplot2>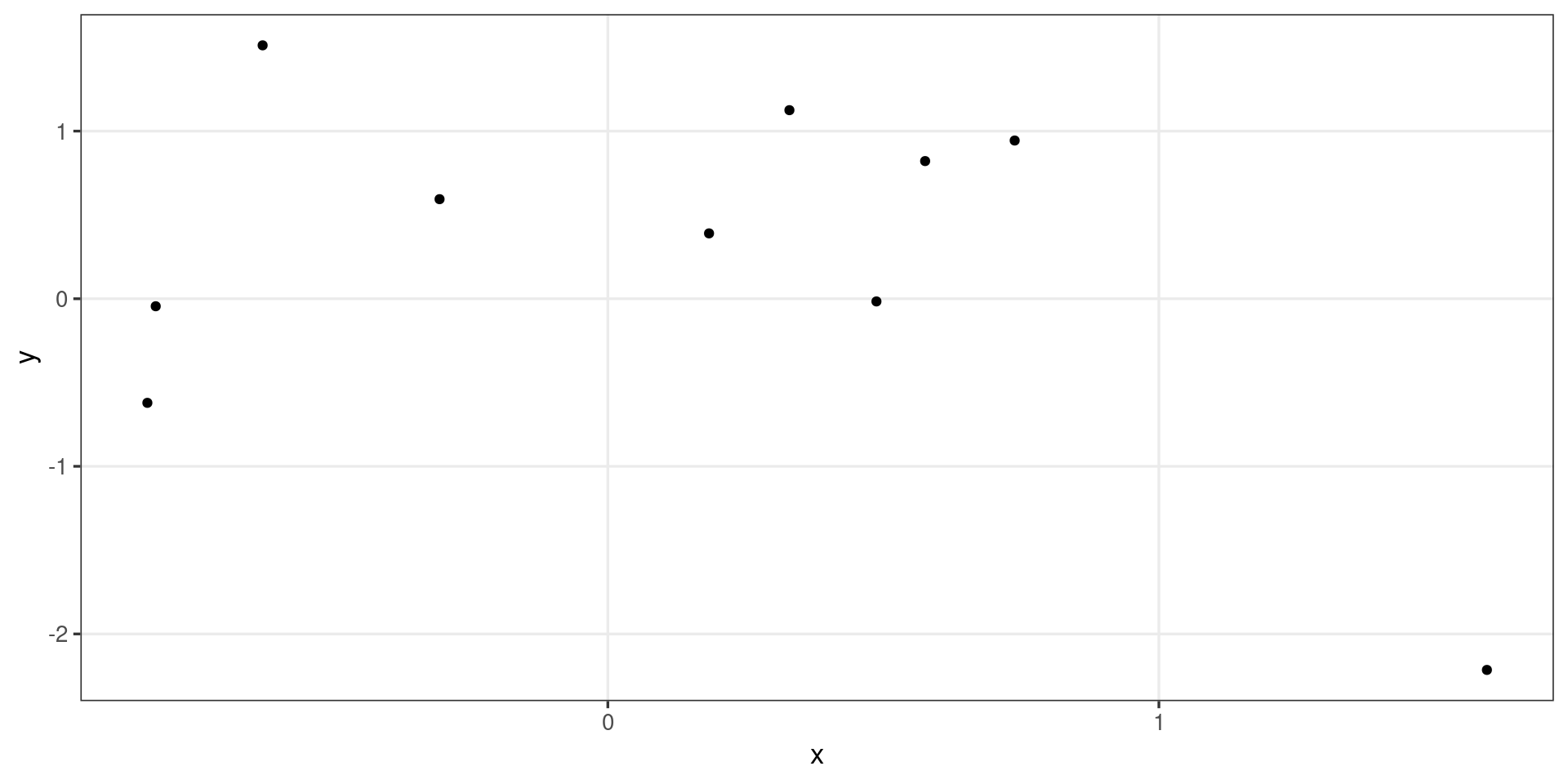
- ggplot2 is built on the ggproto object oriented system.
GeomPointandStatIdentityare each objects* with methods and fields that encode the relevant procedures and defaults to create a scatterplot.
GeomPoint
#> <ggproto object: Class GeomPoint, Geom, gg>
#> aesthetics: function
#> default_aes: uneval
#> draw_group: function
#> draw_key: function
#> draw_layer: function
#> draw_panel: function
#> extra_params: na.rm
#> handle_na: function
#> non_missing_aes: size shape colour
#> optional_aes:
#> parameters: function
#> rename_size: FALSE
#> required_aes: x y
#> setup_data: function
#> setup_params: function
#> use_defaults: function
#> super: <ggproto object: Class Geom, gg>GeomPoint
#> <ggproto object: Class GeomPoint, Geom, gg>
#> aesthetics: function
#> default_aes: uneval
#> draw_group: function
#> draw_key: function
#> draw_layer: function
#> draw_panel: function
#> extra_params: na.rm
#> handle_na: function
#> non_missing_aes: size shape colour
#> optional_aes:
#> parameters: function
#> rename_size: FALSE
#> required_aes: x y
#> setup_data: function
#> setup_params: function
#> use_defaults: function
#> super: <ggproto object: Class Geom, gg>GeomPoint$draw_panel
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_panel(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, panel_params, coord, na.rm = FALSE)
#> {
#> if (is.character(data$shape)) {
#> data$shape <- translate_shape_string(data$shape)
#> }
#> coords <- coord$transform(data, panel_params)
#> stroke_size <- coords$stroke
#> stroke_size[is.na(stroke_size)] <- 0
#> ggname("geom_point", pointsGrob(coords$x, coords$y, pch = coords$shape,
#> gp = gpar(col = alpha(coords$colour, coords$alpha), fill = alpha(coords$fill,
#> coords$alpha), fontsize = coords$size * .pt + stroke_size *
#> .stroke/2, lwd = coords$stroke * .stroke/2)))
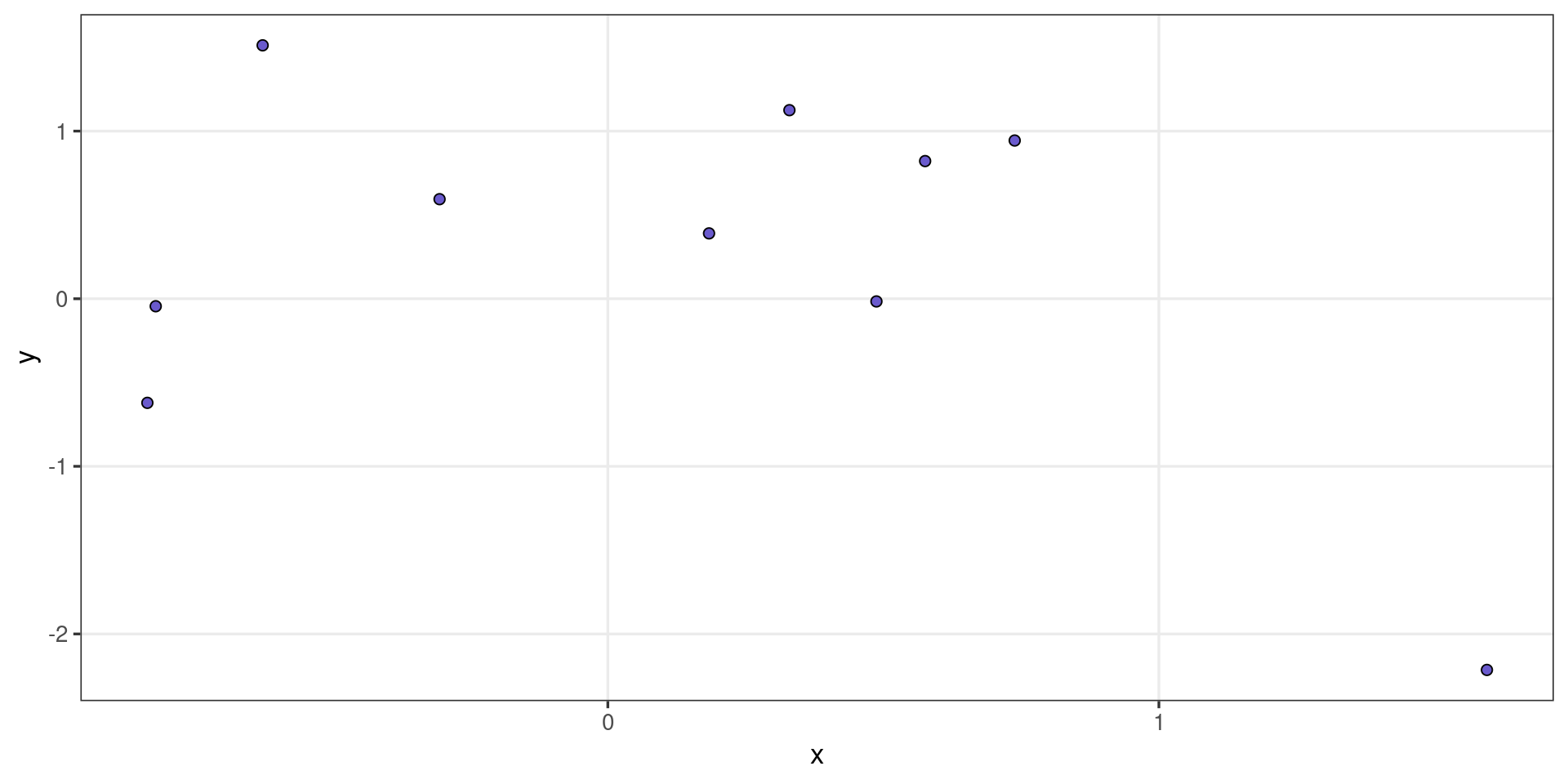
#> }It is simple to extend via inheritance, we can create a GeomPointNew from GeomPoint with a few adjustments to the default aesthetic options:
GeomPointNew
#> <ggproto object: Class GeomPointNew, GeomPoint, Geom, gg>
#> aesthetics: function
#> default_aes: uneval
#> draw_group: function
#> draw_key: function
#> draw_layer: function
#> draw_panel: function
#> extra_params: na.rm
#> handle_na: function
#> non_missing_aes: size shape colour
#> optional_aes:
#> parameters: function
#> rename_size: FALSE
#> required_aes: x y
#> setup_data: function
#> setup_params: function
#> use_defaults: function
#> super: <ggproto object: Class GeomPoint, Geom, gg>GeomPointNew
#> <ggproto object: Class GeomPointNew, GeomPoint, Geom, gg>
#> aesthetics: function
#> default_aes: uneval
#> draw_group: function
#> draw_key: function
#> draw_layer: function
#> draw_panel: function
#> extra_params: na.rm
#> handle_na: function
#> non_missing_aes: size shape colour
#> optional_aes:
#> parameters: function
#> rename_size: FALSE
#> required_aes: x y
#> setup_data: function
#> setup_params: function
#> use_defaults: function
#> super: <ggproto object: Class GeomPoint, Geom, gg>GeomPointNew$draw_panel
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_panel(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, panel_params, coord, na.rm = FALSE)
#> {
#> if (is.character(data$shape)) {
#> data$shape <- translate_shape_string(data$shape)
#> }
#> coords <- coord$transform(data, panel_params)
#> stroke_size <- coords$stroke
#> stroke_size[is.na(stroke_size)] <- 0
#> ggname("geom_point", pointsGrob(coords$x, coords$y, pch = coords$shape,
#> gp = gpar(col = alpha(coords$colour, coords$alpha), fill = alpha(coords$fill,
#> coords$alpha), fontsize = coords$size * .pt + stroke_size *
#> .stroke/2, lwd = coords$stroke * .stroke/2)))
#> }
geom_point_new <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
stat = "identity", position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
data = data,
mapping = mapping,
stat = stat,
geom = GeomPointNew,
position = position,
show.legend = show.legend,
inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(
na.rm = na.rm,
...
)
)
}
Extending stats
(traveling salesperson)
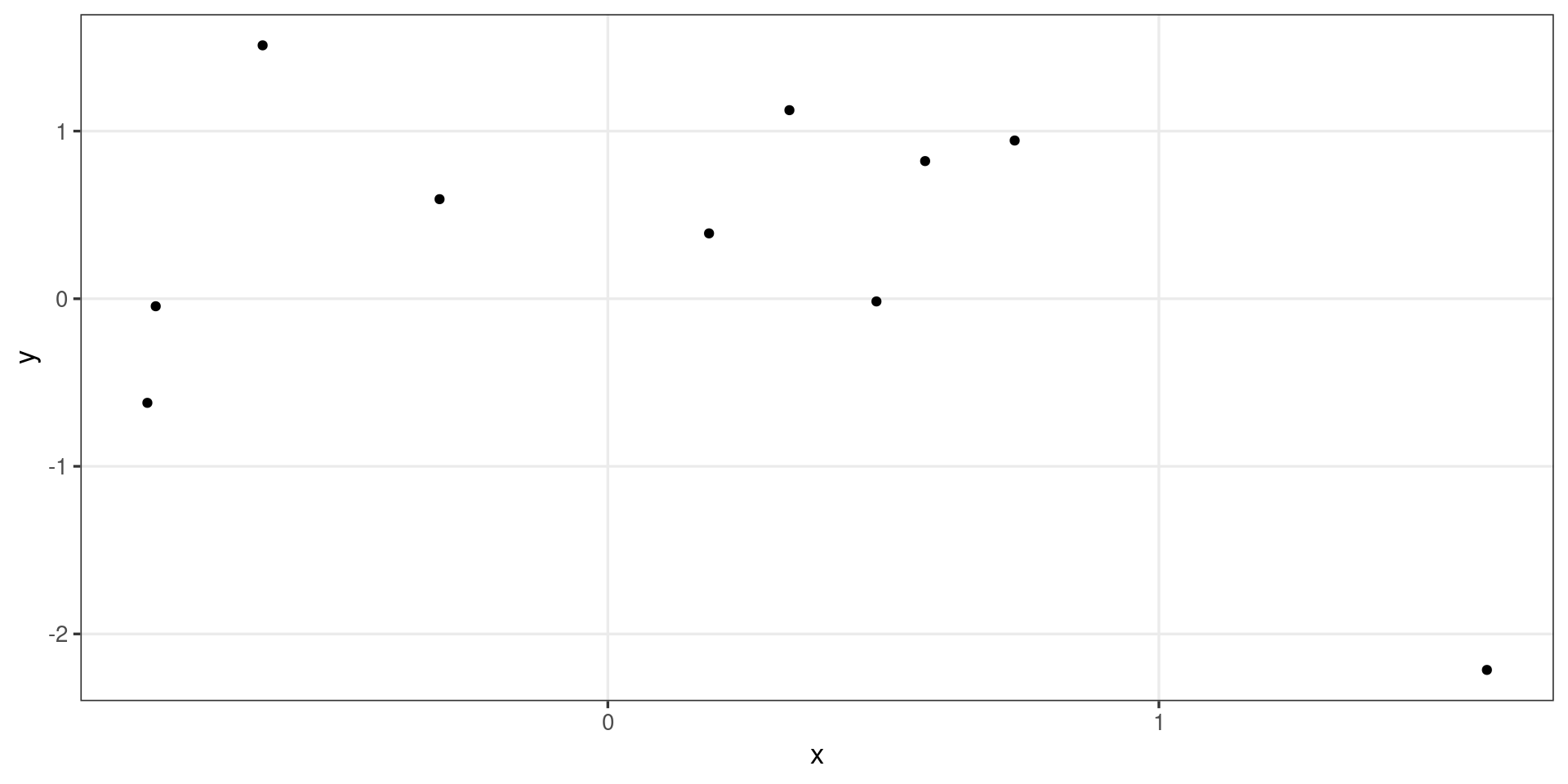
library("TSP")
dist_mat <- dist(df, diag = TRUE, upper = TRUE)
atsp <- as.ATSP(dist_mat)
tour <- solve_TSP(atsp)
str(tour)
#> 'TOUR' Named int [1:10] 8 5 1 10 6 3 4 7 2 9
#> - attr(*, "method")= chr "arbitrary_insertion+two_opt"
#> - attr(*, "tour_length")= num 10.5
#> - attr(*, "names")= chr [1:10] "8" "5" "1" "10" ...
stat_salesperson <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
geom = GeomPath, position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
stat = StatSalesperson, data = data, mapping = mapping, geom = geom,
position = position, show.legend = show.legend, inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(na.rm = na.rm, ...)
)
}
stat_salesperson <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
geom = GeomPath, position = "identity",
...,
method = "nearest_insertion",
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
stat = StatSalesperson,
data = data,
mapping = mapping,
geom = geom,
position = position,
show.legend = show.legend,
inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(
method = method,
na.rm = na.rm,
...
)
)
}


GeomSalesperson <- ggproto("GeomSalesperson", GeomPath)
geom_salesperson <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
stat = StatSalesperson, position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
data = data,
mapping = mapping,
stat = stat,
geom = GeomSalesperson,
position = position,
show.legend = show.legend,
inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(
na.rm = na.rm,
...
)
)
}
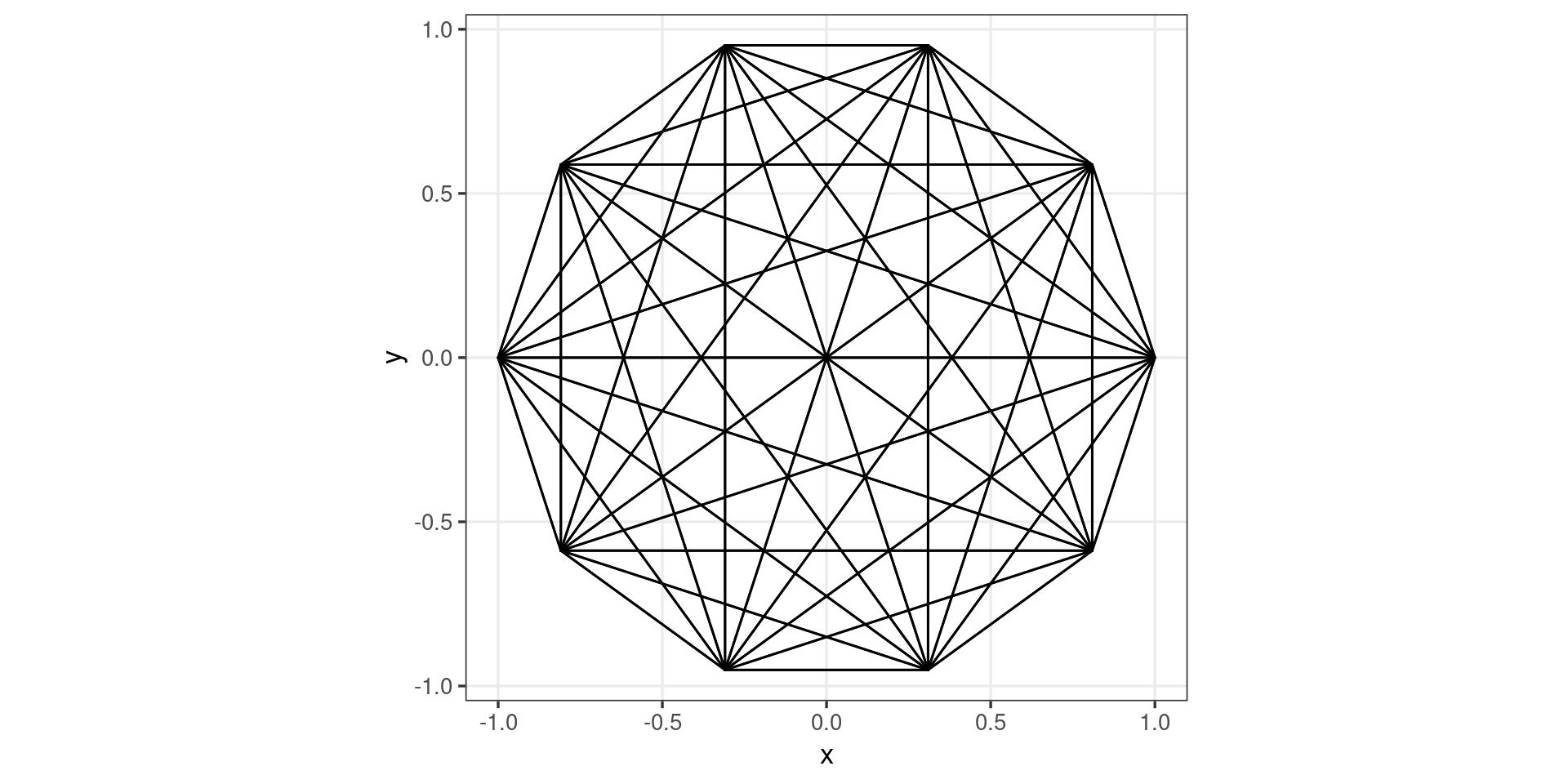
Extending geoms (complete graphs)

A note on “Grobs”
- Grobs are the fundamental building blocks of graphics in R, the “graphical primitives”.
- These are the objects ggplot2’s
Geomclasses use to “draw”. - Paul Murrell’s “R Graphics” is a good resource to learn more about Grobs (and more generally, grid)

GeomSegment$draw_panel
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_panel(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, panel_params, coord, arrow = NULL, arrow.fill = NULL,
#> lineend = "butt", linejoin = "round", na.rm = FALSE)
#> {
#> data <- check_linewidth(data, snake_class(self))
#> data <- remove_missing(data, na.rm = na.rm, c("x", "y", "xend",
#> "yend", "linetype", "linewidth", "shape"), name = "geom_segment")
#> if (empty(data))
#> return(zeroGrob())
#> if (coord$is_linear()) {
#> coord <- coord$transform(data, panel_params)
#> arrow.fill <- arrow.fill %||% coord$colour
#> return(segmentsGrob(coord$x, coord$y, coord$xend, coord$yend,
#> default.units = "native", gp = gpar(col = alpha(coord$colour,
#> coord$alpha), fill = alpha(arrow.fill, coord$alpha),
#> lwd = coord$linewidth * .pt, lty = coord$linetype,
#> lineend = lineend, linejoin = linejoin), arrow = arrow))
#> }
#> data$group <- 1:nrow(data)
#> starts <- subset(data, select = c(-xend, -yend))
#> ends <- rename(subset(data, select = c(-x, -y)), c(xend = "x",
#> yend = "y"))
#> pieces <- vec_rbind0(starts, ends)
#> pieces <- pieces[order(pieces$group), ]
#> GeomPath$draw_panel(pieces, panel_params, coord, arrow = arrow,
#> lineend = lineend)
#> }GeomComplete <- ggproto("GeomComplete", Geom,
required_aes = c("x", "y"),
default_aes = aes(
colour = "black",
linewidth = 0.5,
linetype = 1,
alpha = NA
),
non_missing_aes = c("linetype", "linewidth", "shape"),
draw_group = function(data, panel_params, coord) {
data_expanded <- data[rep(1:nrow(data), each = nrow(data)), ]
data_expanded$xend <- rep(data$x, times = nrow(data))
data_expanded$yend <- rep(data$y, times = nrow(data))
coord <- coord$transform(data_expanded, panel_params)
grid::segmentsGrob(coord$x, coord$y, coord$xend, coord$yend,
default.units = "native",
gp = grid::gpar(
col = alpha(coord$colour, coord$alpha),
fill = alpha(coord$colour, coord$alpha),
lwd = coord$linewidth * .pt,
lty = coord$linetype
)
)
},
draw_key = draw_key_path
)geom_complete <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
stat = StatIdentity, position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
data = data,
mapping = mapping,
stat = stat,
geom = GeomComplete,
position = position,
show.legend = show.legend,
inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(
na.rm = na.rm,
...
)
)
}
An aside: Stat vs Geom implementations
Stats are used for transformations1 of dataGeoms are used for converting data structures into their visual representations2
An aside: Stat vs Geom implementations
Things to consider when deciding which to implement:
- Can you implement a
Statwhich “plugs in” to an existingGeom? (e.g.StatSalespersonandGeomSegment)? - Would a user rather have the ability to specify an alternate
StatorGeom? - Which is easier? (typically, the
Statimplementation) - Do you need both?
Why extend?
Revisiting the traveling salesperson problem, we saw previously that we can easily perform the necessary calculations outside of ggplot2; avoiding the hassle of defining GeomSalesperson and friends:
What if we want to plot multiple groups?
What if we want to plot multiple groups?
Split, Apply, Combine!

# Split
df_split <- split(df_mult[,c("x", "y")], df_mult$class)
str(df_split)
#> List of 3
#> $ a:'data.frame': 10 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x: num [1:10] -0.626 0.184 -0.836 1.595 0.33 ...
#> ..$ y: num [1:10] 1.3587 -0.1028 0.3877 -0.0538 -1.3771 ...
#> $ b:'data.frame': 10 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x: num [1:10] 1.512 0.39 -0.621 -2.215 1.125 ...
#> ..$ y: num [1:10] -0.165 -0.253 0.697 0.557 -0.689 ...
#> $ c:'data.frame': 10 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x: num [1:10] 0.919 0.7821 0.0746 -1.9894 0.6198 ...
#> ..$ y: num [1:10] 0.398 -0.612 0.341 -1.129 1.433 ...# Apply
class_sols <-
df_split |>
lapply(dist, diag = TRUE, upper = TRUE) |>
lapply(as.ATSP) |>
lapply(solve_TSP)
str(class_sols)
#> List of 3
#> $ a: 'TOUR' Named int [1:10] 10 3 6 5 7 2 8 4 9 1
#> ..- attr(*, "method")= chr "arbitrary_insertion+two_opt"
#> ..- attr(*, "tour_length")= num 9.23
#> ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:10] "10" "3" "6" "5" ...
#> $ b: 'TOUR' Named int [1:10] 10 7 3 4 6 2 5 1 9 8
#> ..- attr(*, "method")= chr "arbitrary_insertion+two_opt"
#> ..- attr(*, "tour_length")= num 9.68
#> ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:10] "20" "17" "13" "14" ...
#> $ c: 'TOUR' Named int [1:10] 3 9 4 8 7 10 2 1 5 6
#> ..- attr(*, "method")= chr "arbitrary_insertion+two_opt"
#> ..- attr(*, "tour_length")= num 10.7
#> ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:10] "23" "29" "24" "28" ...# Apply
reorder_rows_by_indices <- function(df, i) df[i,]
df_split_ordered <- Map(reorder_rows_by_indices, df_split, class_sols)
str(df_split_ordered)
#> List of 3
#> $ a:'data.frame': 10 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x: num [1:10] -0.305 -0.836 -0.82 0.33 0.487 ...
#> ..$ y: num [1:10] 0.763 0.388 -0.415 -1.377 -0.394 ...
#> $ b:'data.frame': 10 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x: num [1:10] 0.5939 -0.0162 -0.6212 -2.2147 -0.0449 ...
#> ..$ y: num [1:10] 0.881 0.365 0.697 0.557 -0.707 ...
#> $ c:'data.frame': 10 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x: num [1:10] 0.0746 -0.4782 -1.9894 -1.4708 -0.1558 ...
#> ..$ y: num [1:10] 0.341 0.57 -1.129 -1.044 -0.367 ...
# Split
df_split <- split(df_mult[,c("x", "y")], df_mult$class)
# Apply
class_sols <-
df_split |>
lapply(dist, diag = TRUE, upper = TRUE) |>
lapply(as.ATSP) |>
lapply(solve_TSP)
reorder_rows_by_indices <- function(df, i) df[i,]
df_split_ordered <- Map(reorder_rows_by_indices, df_split, class_sols)
# Combine
df_mult_ordered <- unsplit(df_split_ordered, df_mult$class)
df_mult_ordered$class <- df_mult$classInstead, we can let ggplot2 do this for us!

Understanding the internals
ggplot2 is using the same split-apply-combine strategy for each layer, $compute_layer() and $draw_layer() methods call $compute_panel() or $draw_panel() for each class!
GeomComplete$draw_layer
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_layer(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, params, layout, coord)
#> {
#> if (empty(data)) {
#> n <- if (is.factor(data$PANEL))
#> nlevels(data$PANEL)
#> else 1L
#> return(rep(list(zeroGrob()), n))
#> }
#> params <- params[intersect(names(params), self$parameters())]
#> if (nlevels(as.factor(data$PANEL)) > 1L) {
#> data_panels <- split(data, data$PANEL)
#> }
#> else {
#> data_panels <- list(data)
#> }
#> lapply(data_panels, function(data) {
#> if (empty(data))
#> return(zeroGrob())
#> panel_params <- layout$panel_params[[data$PANEL[1]]]
#> inject(self$draw_panel(data, panel_params, coord, !!!params))
#> })
#> }StatSalesperson$compute_layer
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> compute_layer(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, params, layout)
#> {
#> check_required_aesthetics(self$required_aes, c(names(data),
#> names(params)), snake_class(self))
#> required_aes <- intersect(names(data), unlist(strsplit(self$required_aes,
#> "|", fixed = TRUE)))
#> data <- remove_missing(data, params$na.rm, c(required_aes,
#> self$non_missing_aes), snake_class(self), finite = TRUE)
#> params <- params[intersect(names(params), self$parameters())]
#> args <- c(list(data = quote(data), scales = quote(scales)),
#> params)
#> dapply(data, "PANEL", function(data) {
#> scales <- layout$get_scales(data$PANEL[1])
#> try_fetch(inject(self$compute_panel(data = data, scales = scales,
#> !!!params)), error = function(cnd) {
#> cli::cli_warn("Computation failed in {.fn {snake_class(self)}}",
#> parent = cnd)
#> data_frame0()
#> })
#> })
#> }Additional Resources
- ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis by Hadley Wickham
- The third edition has a chapter on writing extensions
vignette("extending-ggplot2")- ggplot2’s source code
- Also, the source code of ggplot2 extensions
- ggtrace for interactive debugging of ggplot2 internals
- R Graphics by Paul Murrell
Thank you!
Details
Prototypes
Prototypes
- Technically,
Stats andGeoms are not classes; they are prototypes.
- This does not come up frequently, but it can lead to unexpected behavior
is.environment(GeomComplete)
#> [1] TRUE
# Only see what we set, not what we inherited:
ls(GeomComplete)
#> [1] "default_aes" "draw_group" "draw_key" "non_missing_aes"
#> [5] "required_aes" "super"
GeomComplete$draw_layer
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_layer(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, params, layout, coord)
#> {
#> if (empty(data)) {
#> n <- if (is.factor(data$PANEL))
#> nlevels(data$PANEL)
#> else 1L
#> return(rep(list(zeroGrob()), n))
#> }
#> params <- params[intersect(names(params), self$parameters())]
#> if (nlevels(as.factor(data$PANEL)) > 1L) {
#> data_panels <- split(data, data$PANEL)
#> }
#> else {
#> data_panels <- list(data)
#> }
#> lapply(data_panels, function(data) {
#> if (empty(data))
#> return(zeroGrob())
#> panel_params <- layout$panel_params[[data$PANEL[1]]]
#> inject(self$draw_panel(data, panel_params, coord, !!!params))
#> })
#> }coord$transform()
GeomPoint$draw_panel
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_panel(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, panel_params, coord, na.rm = FALSE)
#> {
#> if (is.character(data$shape)) {
#> data$shape <- translate_shape_string(data$shape)
#> }
#> coords <- coord$transform(data, panel_params)
#> stroke_size <- coords$stroke
#> stroke_size[is.na(stroke_size)] <- 0
#> ggname("geom_point", pointsGrob(coords$x, coords$y, pch = coords$shape,
#> gp = gpar(col = alpha(coords$colour, coords$alpha), fill = alpha(coords$fill,
#> coords$alpha), fontsize = coords$size * .pt + stroke_size *
#> .stroke/2, lwd = coords$stroke * .stroke/2)))
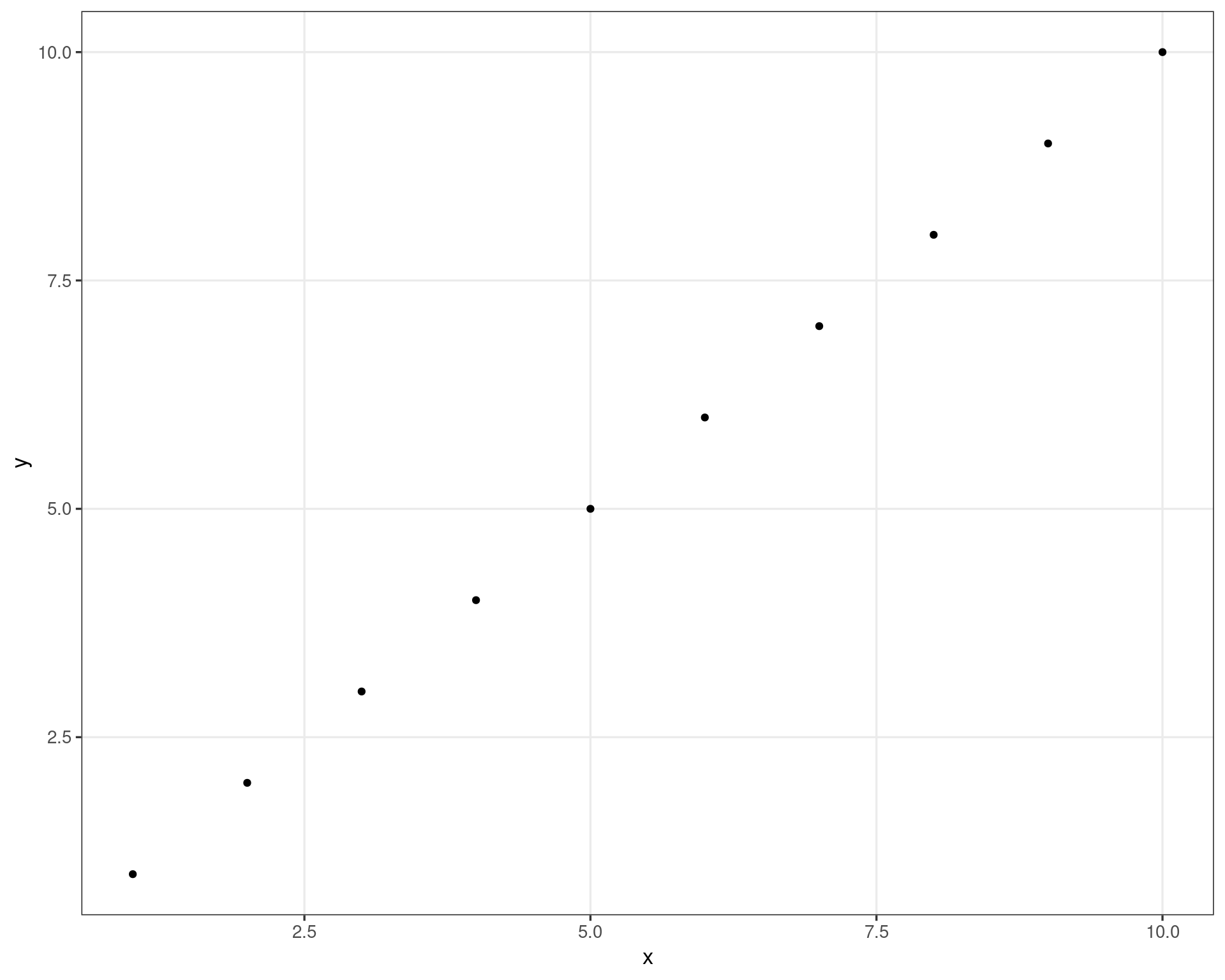
#> }df <- data.frame(
x = 1:10,
y = 1:10
)
range(df$x)
#> [1] 1 10
range(df$y)
#> [1] 1 10
# default from scale_x/y_continuous()
scales::expand_range(c(1, 10), .05)
#> [1] 0.55 10.45
ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
geom_rect(
xmin = .55, xmax = 10.45,
ymin = .55, ymax = 10.45,
color = "red", fill = NA,
linewidth = 1
)
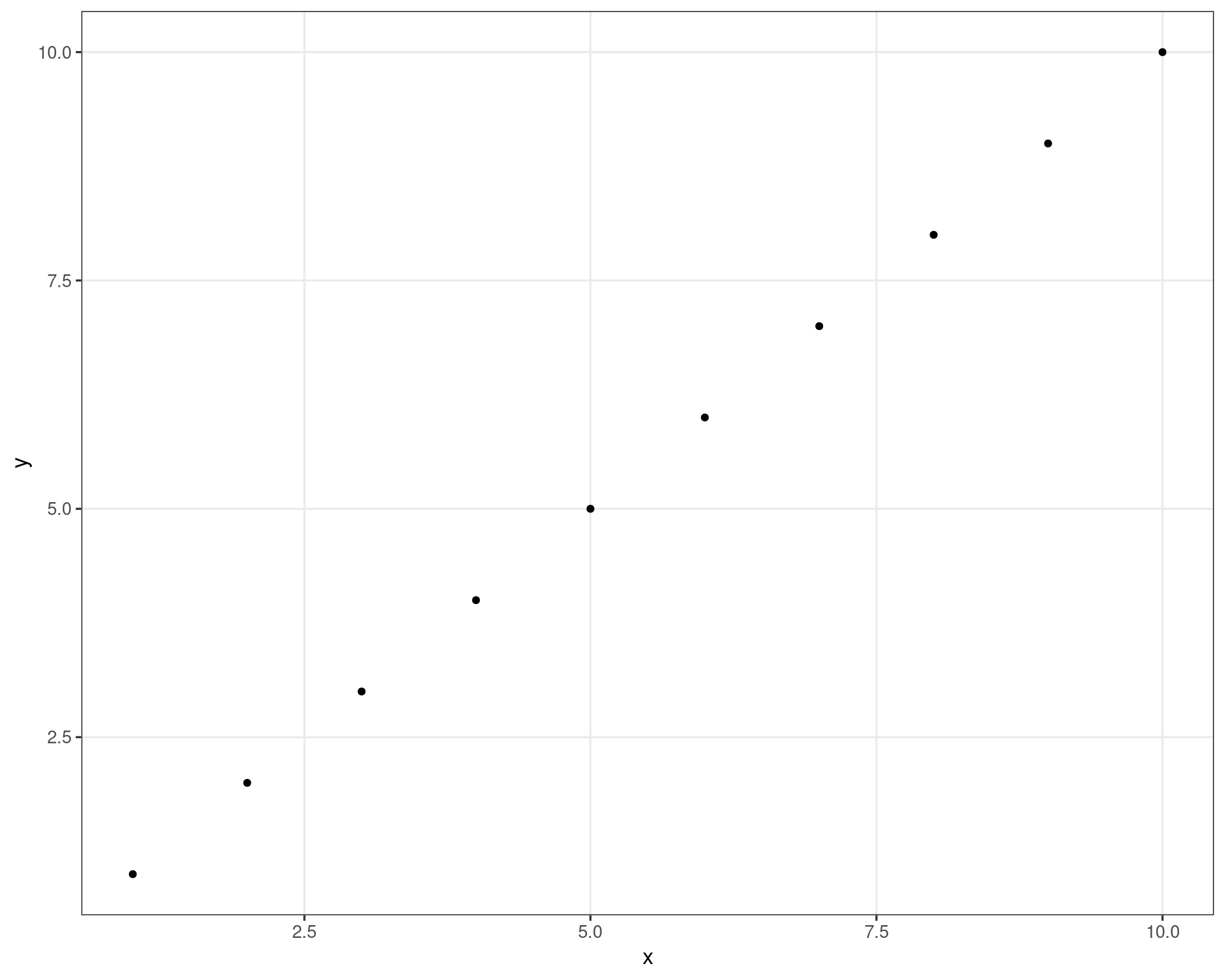
df <- data.frame(
x = 1:10,
y = 1:10
)
ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
theme(
axis.title = element_blank(),
axis.text = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.length = unit(0, "npc"),
plot.margin = margin()
)
grid::grid.points(
x = grid::unit(1/2, "npc"),
y = grid::unit(1/2, "npc")
)
grid::grid.points(
x = grid::unit(c(0, 0, 1, 1), "npc"),
y = grid::unit(c(0, 1, 0, 1), "npc"),
gp = grid::gpar(col = "red")
)
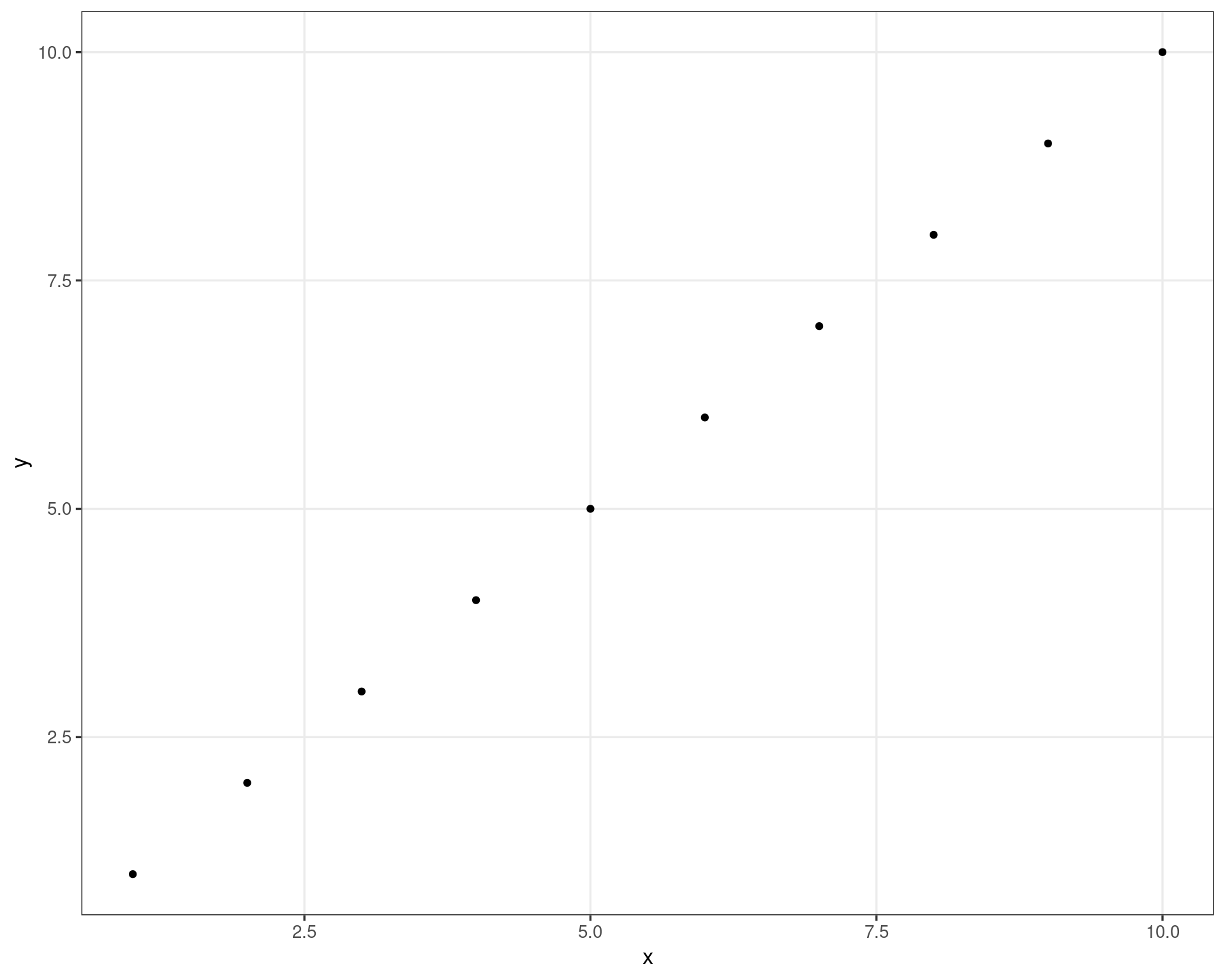
df <- data.frame(
x = 1:10,
y = 1:10
)
ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
theme(
axis.title = element_blank(),
axis.text = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.length = unit(0, "npc"),
plot.margin = margin()
)
# transform from the data coordinates
# to the plotting coordinates (npc)
df_rescaled <- df |>
mutate(
x = scales::rescale(x,
to = c(0, 1), from = c(.55, 10.45)),
y = scales::rescale(y,
to = c(0, 1), from = c(.55, 10.45))
)
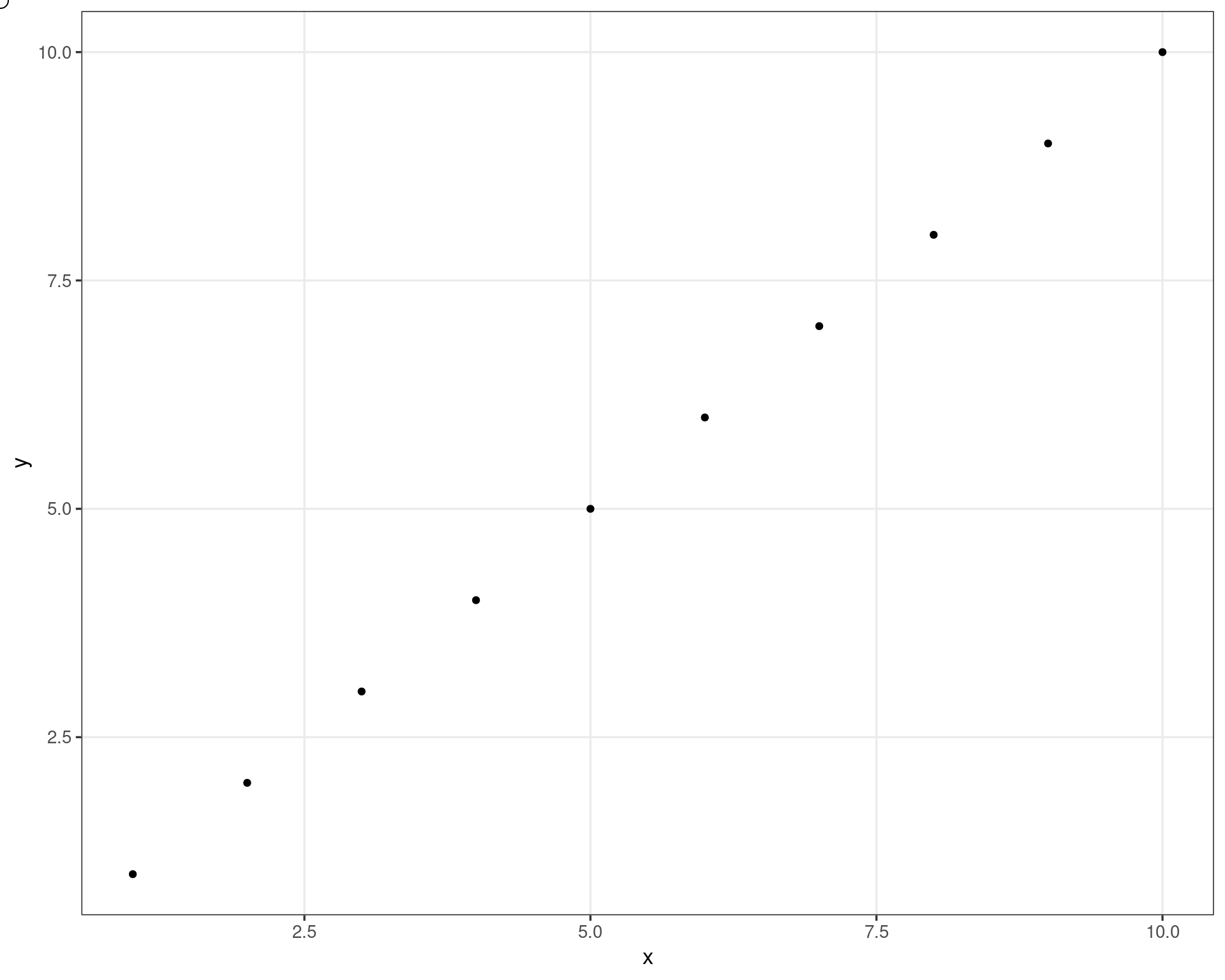
df <- data.frame(
x = 1:10,
y = 1:10
)
ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
theme(
axis.title = element_blank(),
axis.text = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.length = unit(0, "npc"),
plot.margin = margin()
)
# transform from the data coordinates
# to the plotting coordinates (npc)
df_rescaled <- df |>
mutate(
x = scales::rescale(x,
to = c(0, 1), from = c(.55, 10.45)),
y = scales::rescale(y,
to = c(0, 1), from = c(.55, 10.45))
)
grid::grid.points(
x = grid::unit(df_rescaled$x, "npc"),
y = grid::unit(df_rescaled$y, "npc")
)
GeomPoint$draw_panel
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> draw_panel(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, data, panel_params, coord, na.rm = FALSE)
#> {
#> if (is.character(data$shape)) {
#> data$shape <- translate_shape_string(data$shape)
#> }
#> coords <- coord$transform(data, panel_params)
#> stroke_size <- coords$stroke
#> stroke_size[is.na(stroke_size)] <- 0
#> ggname("geom_point", pointsGrob(coords$x, coords$y, pch = coords$shape,
#> gp = gpar(col = alpha(coords$colour, coords$alpha), fill = alpha(coords$fill,
#> coords$alpha), fontsize = coords$size * .pt + stroke_size *
#> .stroke/2, lwd = coords$stroke * .stroke/2)))
#> }ggplot2:::CoordCartesian$transform
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> transform(...)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (data, panel_params)
#> {
#> data <- transform_position(data, panel_params$x$rescale,
#> panel_params$y$rescale)
#> transform_position(data, squish_infinite, squish_infinite)
#> }# Can debug interactively with {ggtrace}
# to learn about `panel_params$x/y$rescale()`
ggtrace::ggdebugonce(ggplot2:::CoordCartesian$transform)
panel_params$x$rescale
#> <ggproto method>
#> <Wrapper function>
#> function (...)
#> rescale(..., self = self)
#>
#> <Inner function (f)>
#> function (self, x)
#> {
#> self$scale$rescale(x, self$limits, self$continuous_range)
#> }Avoiding grid with $setup_data()
The
$setup_data()method allowsGeoms to “intercept” the layer’s data before the$draw_*()hierarchyThis is of limited use, mainly for “row-wise” operations
We can attempt to implement
GeomCompletewith this strategy, however we will quickly run into problems
GeomComplete <- ggproto("GeomComplete", GeomSegment,
required_aes = c("x", "y"),
setup_data = function(data, params) {
data_expanded <- data[rep(1:nrow(data), each = nrow(data)), ]
data_expanded$xend <- rep(data$x, times = nrow(data))
data_expanded$yend <- rep(data$y, times = nrow(data))
data_expanded
}
)
# Need to be careful: `$setup_data()`
# is not split-apply-combine'd
df_circles <- data.frame(
x = cos(seq(0, 2*pi, length.out = 16))[-16],
y = sin(seq(0, 2*pi, length.out = 16))[-16],
class = rep(c("a", "b", "c"), times = 5)
)
ggplot(df_circles) +
geom_complete(aes(x, y, color = class)) +
geom_point_new(aes(x, y, fill = class), size = 3) +
coord_fixed()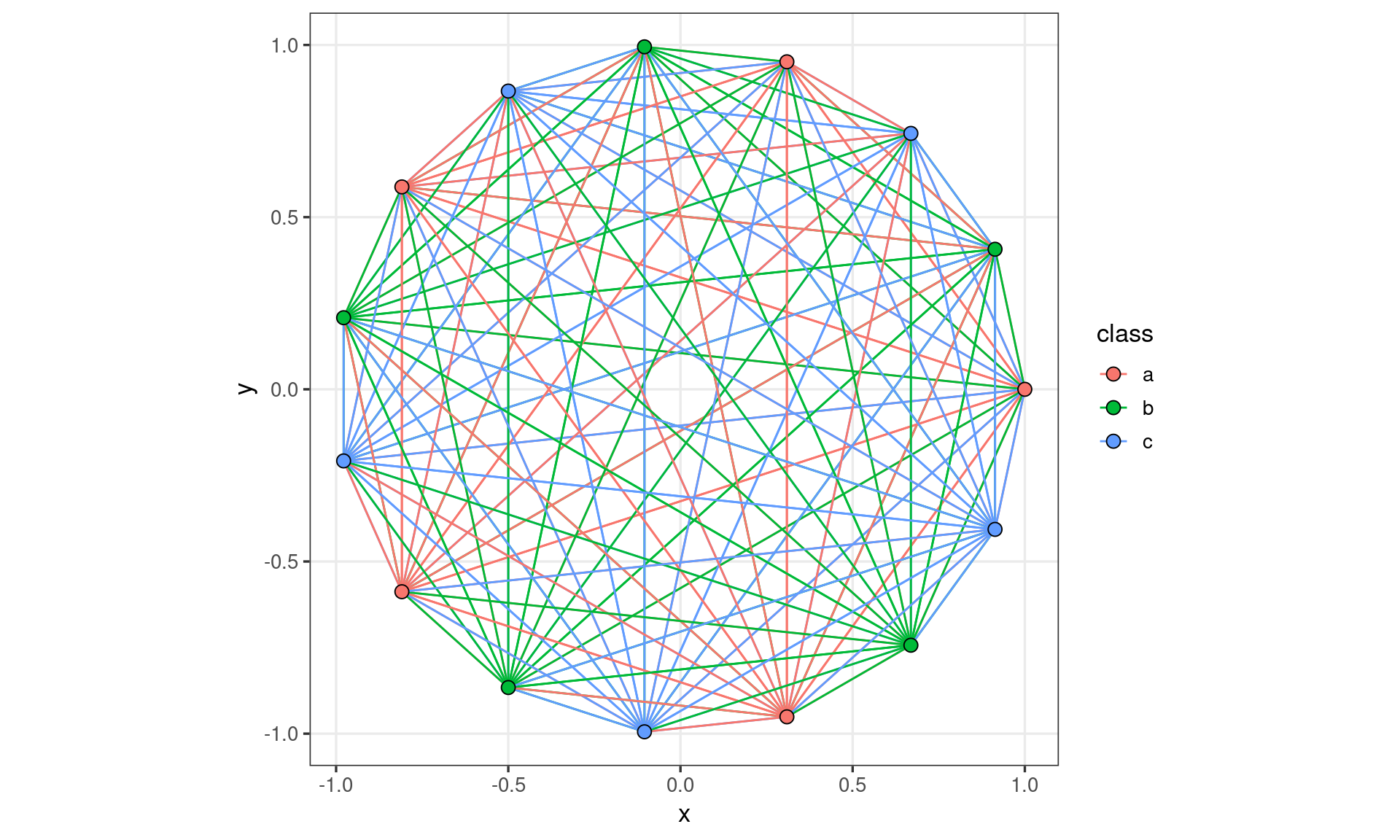
Another way to avoid grid
We can use existing
$draw_layer(),$draw_panel(), and$draw_group()methods in newGeomobjects.This allows a much easier (and less error-prone) implementation of
GeomComplete
GeomComplete <- ggproto("GeomComplete", Geom,
required_aes = c("x", "y"),
default_aes = aes(
colour = "black",
linewidth = 0.5,
linetype = 1,
alpha = NA
),
non_missing_aes = c("linetype", "linewidth", "shape"),
draw_group = function(data, panel_params, coord, ...) {
data_expanded <- data[rep(1:nrow(data), each = nrow(data)), ]
data_expanded$xend <- rep(data$x, times = nrow(data))
data_expanded$yend <- rep(data$y, times = nrow(data))
# hand group-level data off to GeomSegment$draw_panel()
GeomSegment$draw_panel(data_expanded, panel_params, coord, ...)
},
draw_key = draw_key_path
)Other ways to extend ggplot2
- Aside from implementing new
GeomandStatggprotoobjects, there are other formal ways to extend ggplot2:- New color palettes for
scale_color/fill() - Customized themes
- New coordinate systems
- New scales
- New faceting systems
- New color palettes for


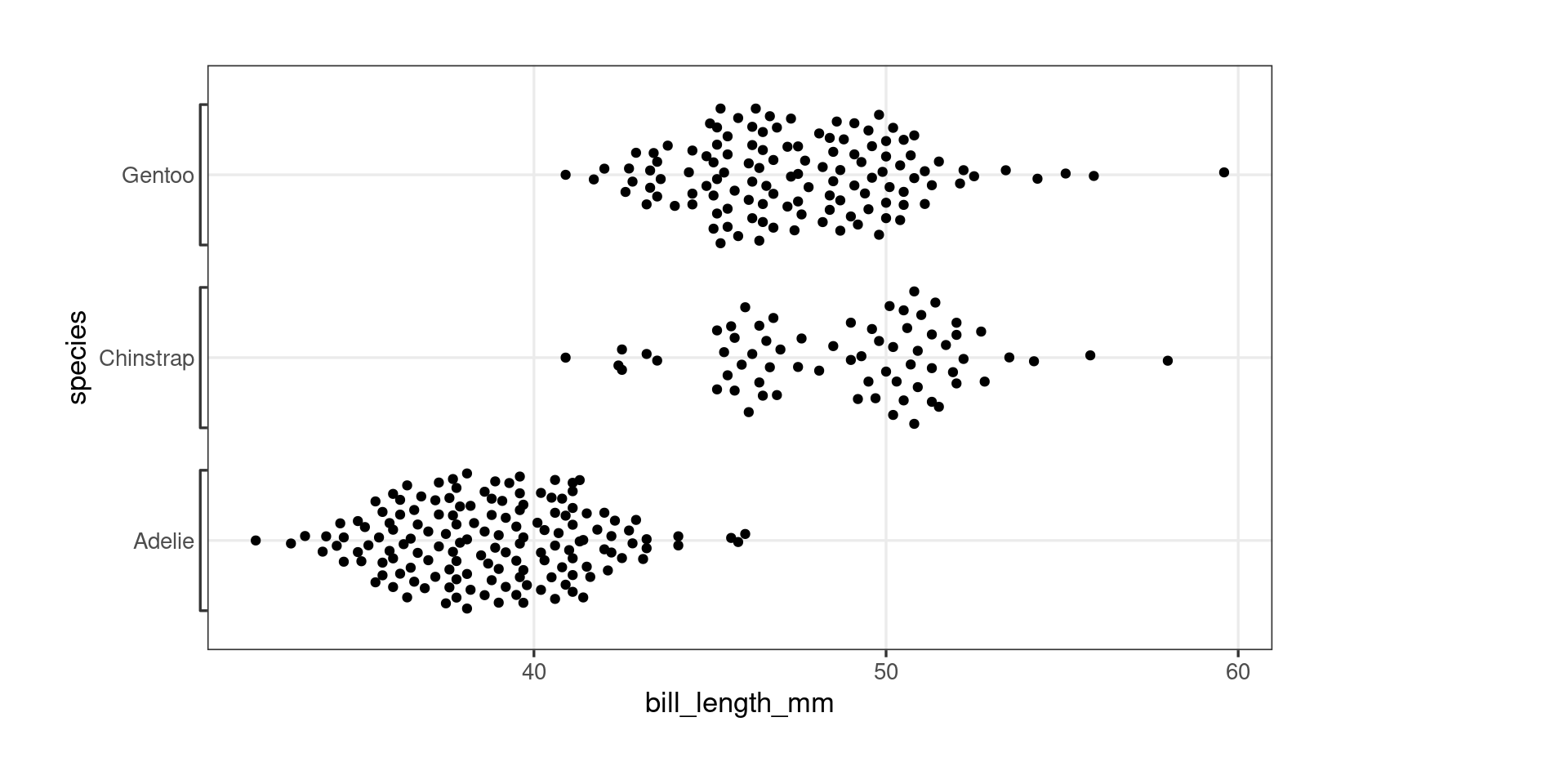
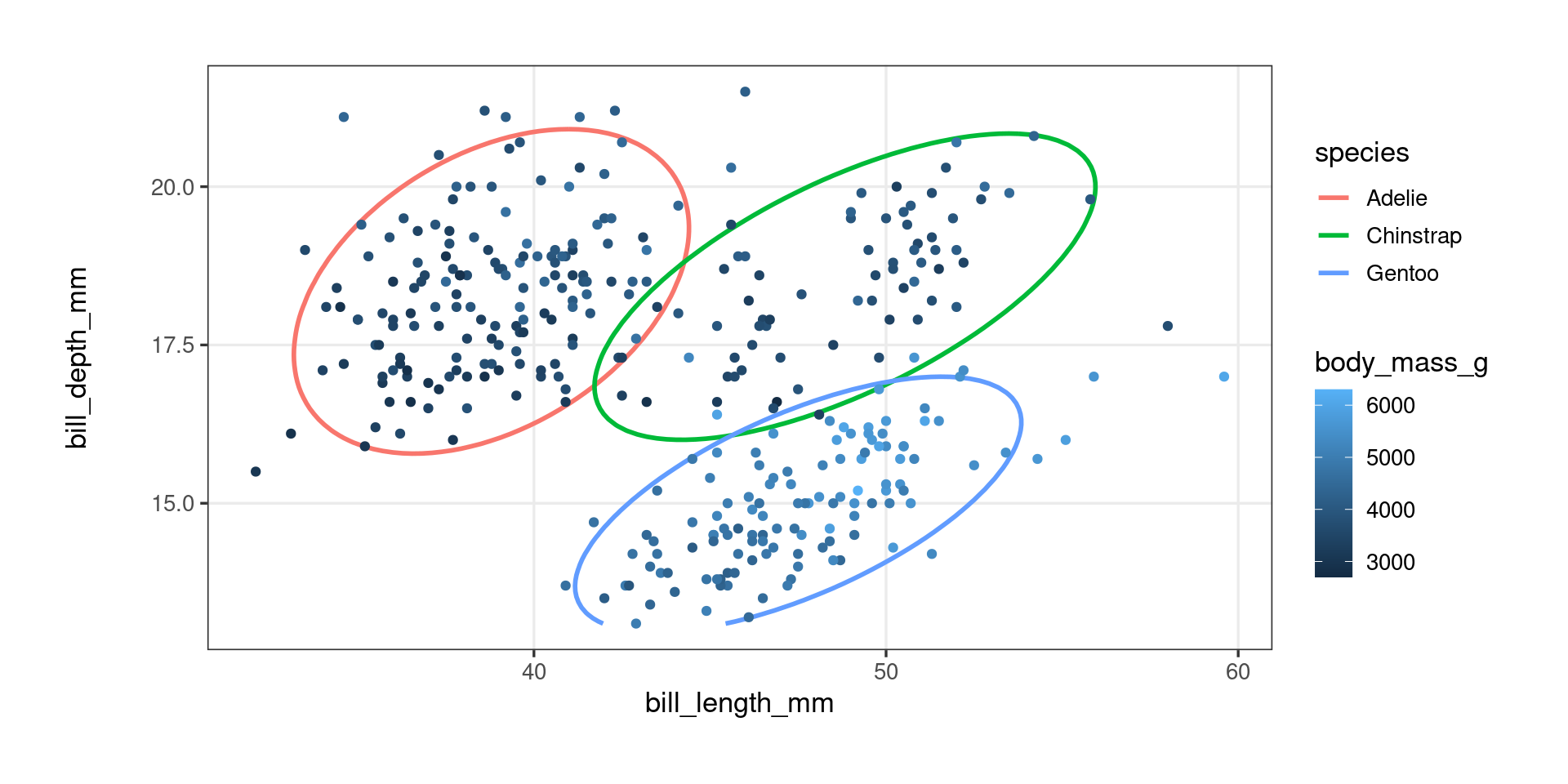
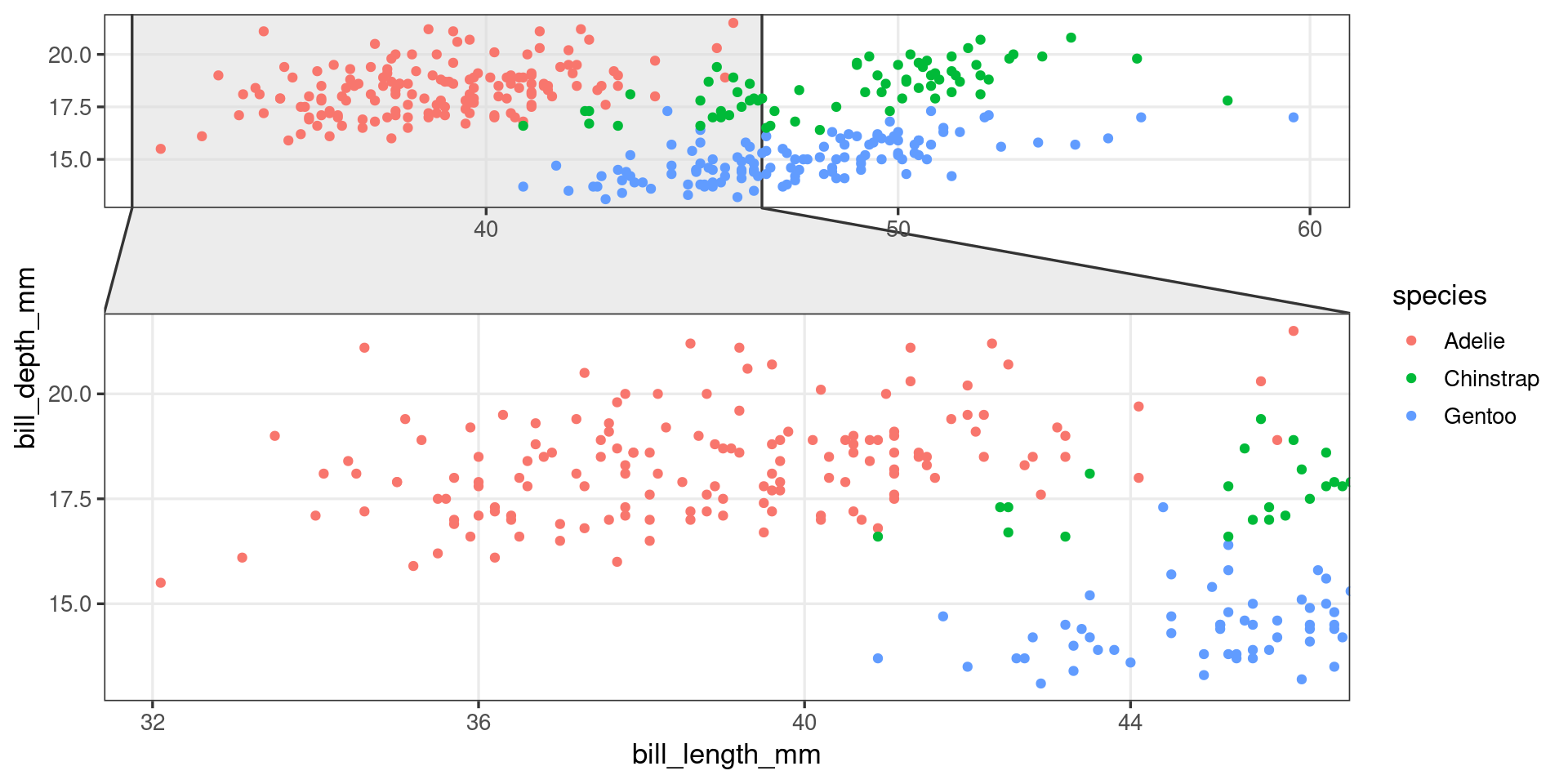

Package development – ggproto
R packages for ggplot2 extensions look slightly different than most other packages1
These packages export functions as well as
ggprotoobjectsPractically, this has little impact on the package development workflow and the code’s organization
Example:
ggdensity::GeomHdr’s source code
Package development – documentation
- It is easiest to inherit parameter documentation where possible
- Almost always inherit from
ggplot2::stat_identity() - Sometimes from relevant
Geoms (e.g.ggplot2::geom_segment()) - Sometimes from workhorse computational packages (e.g.
TSP::solve_tsp())
- Almost always inherit from
- Layer functions should have sections: “Aesthetics” and “Computed variables”
- This is in addition to the typical sections (e.g. description, arguments, examples)
- Group all related functions/objects into a single topic
- e.g.
?geom_hdr,?stat_hdr,?GeomHdr, and?StatHdrare the same
- e.g.
#' Highest density regions of a 2D density estimate
#'
#' Perform 2D density estimation, compute and plot the resulting highest density regions.
#' `geom_hdr()` draws filled regions and `geom_hdr_lines()` draws lines outlining the regions.
#' Note, the plotted objects have probabilities mapped to the `alpha` aesthetic by default.
#'
#' @section Aesthetics: `geom_hdr()` and `geom_hdr_lines()` understand the following aesthetics (required
#' aesthetics are in bold):
#'
#' - **x**
#' - **y**
#' - alpha
#' - color
#' - fill (only `geom_hdr`)
#' - group
#' - linetype
#' - linewidth
#' - subgroup
#'
#' @section Computed variables:
#'
#' \describe{ \item{probs}{The probability associated with the highest density region, specified
#' by `probs` argument.} }
#'
#' @inheritParams ggplot2::geom_path
#' @inheritParams ggplot2::stat_identity
#' @inheritParams ggplot2::stat_density2d
#' @param method Density estimator to use, accepts character vector:
#' `"kde"`,`"histogram"`, `"freqpoly"`, or `"mvnorm"`.
#' Alternatively accepts functions which return closures corresponding to density estimates,
#' see `?get_hdr` or `vignette("method", "ggdensity")`.
#' @param probs Probabilities to compute highest density regions for.
#' @param xlim,ylim Range to compute and draw regions. If `NULL`, defaults to
#' range of data.
#' @param n Resolution of grid defined by `xlim` and `ylim`.
#' Ignored if `method = "histogram"` or `method = "freqpoly"`.
#' @name geom_hdr
#' @rdname geom_hdr
#' @references Scott, David W. Multivariate Density Estimation (2e), Wiley.
#'
#' @import ggplot2
#'
#' @examples
#' # Basic simulated data with bivariate normal data and various methods
#' df <- data.frame(x = rnorm(1000), y = rnorm(1000))
#' p <- ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) + coord_equal()
#'
#' p + geom_hdr()
#' p + geom_hdr(method = "mvnorm")
#' p + geom_hdr(method = "freqpoly")
#' # p + geom_hdr(method = "histogram")
#'
#' # Adding point layers on top to visually assess region estimates
#' pts <- geom_point(size = .2, color = "red")
#'
#' p + geom_hdr() + pts
#' p + geom_hdr(method = "mvnorm") + pts
#' p + geom_hdr(method = "freqpoly") + pts
#' # p + geom_hdr(method = "histogram") + pts
#'
#' # Highest density region boundary lines
#' p + geom_hdr_lines()
#' p + geom_hdr_lines(method = "mvnorm")
#' p + geom_hdr_lines(method = "freqpoly")
#' # p + geom_hdr_lines(method = "histogram")
#'
#' \dontrun{
#'
#' # 2+ groups - mapping other aesthetics in the geom
#' rdata <- function(n, n_groups = 3, radius = 3) {
#' list_of_dfs <- lapply(0:(n_groups-1), function(k) {
#' mu <- c(cos(2*k*pi/n_groups), sin(2*k*pi/n_groups))
#' m <- MASS::mvrnorm(n, radius*mu, diag(2))
#' structure(data.frame(m, as.character(k)), names = c("x", "y", "c"))
#' })
#' do.call("rbind", list_of_dfs)
#' }
#'
#' dfc <- rdata(1000, n_groups = 5)
#' pf <- ggplot(dfc, aes(x, y, fill = c)) + coord_equal()
#'
#' pf + geom_hdr()
#' pf + geom_hdr(method = "mvnorm")
#' pf + geom_hdr(method = "mvnorm", probs = .90, alpha = .5)
#' pf + geom_hdr(method = "histogram")
#' pf + geom_hdr(method = "freqpoly")
#'
#' pc <- ggplot(dfc, aes(x, y, color = c)) +
#' coord_equal() +
#' theme_minimal() +
#' theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank())
#'
#' pc + geom_hdr_lines()
#' pc + geom_hdr_lines(method = "mvnorm")
#'
#'
#' # Data with boundaries
#' ggplot(df, aes(x^2)) + geom_histogram(bins = 30)
#' ggplot(df, aes(x^2)) + geom_histogram(bins = 30, boundary = 0)
#' ggplot(df, aes(x^2, y^2)) + geom_hdr(method = "histogram")
#'
#' }
#'
NULL
#' @rdname geom_hdr
#' @export
stat_hdr <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
geom = "hdr", position = "identity",
...,
method = "kde",
probs = c(.99, .95, .8, .5),
n = 100,
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
data = data,
mapping = mapping,
stat = StatHdr,
geom = geom,
position = position,
show.legend = show.legend,
inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(
method = method,
probs = probs,
n = n,
xlim = xlim,
ylim = ylim,
na.rm = na.rm,
...
)
)
}
#' @rdname geom_hdr
#' @format NULL
#' @usage NULL
#' @importFrom scales percent
#' @export
StatHdr <- ggproto("StatHdr", Stat,
required_aes = c("x", "y"),
default_aes = aes(order = after_stat(probs), alpha = after_stat(probs)),
output = "bands",
compute_group = function(self, data, scales, na.rm = FALSE,
method = "kde", probs = c(.99, .95, .8, .5),
n = 100, xlim = NULL, ylim = NULL) {
rangex <- xlim %||% scales$x$dimension()
rangey <- ylim %||% scales$y$dimension()
# Only calculate HDR membership if we need to
need_membership <- (self$output == "points")
res <- get_hdr(data, method, probs, n, rangex, rangey, hdr_membership = need_membership)
res_to_df(res, probs, data$group[1], self$output)
}
)
# internal helper function to convert output of `get_hdr[_1d]()` into
# what `GeomHdr*$draw_group()` methods need
res_to_df <- function(res, probs, group, output) {
# Need z for xyz_to_isobands/lines()
res$df_est$z <- res$df_est$fhat
if (output == "bands") {
isobands <- xyz_to_isobands(res$df_est, res$breaks)
names(isobands) <- scales::percent_format(accuracy = 1)(probs)
df <- iso_to_polygon(isobands, group)
df$probs <- ordered(df$level, levels = names(isobands))
df$level <- NULL
} else if (output == "lines") {
isolines <- xyz_to_isolines(res$df_est, res$breaks)
names(isolines) <- scales::percent_format(accuracy = 1)(probs)
df <- iso_to_path(isolines, group)
df$probs <- ordered(df$level, levels = names(isolines))
df$level <- NULL
} else if (output == "points") {
df <- res$data
df$hdr_membership <- scales::percent_format(accuracy = 1)(df$hdr_membership)
df$probs <- ordered(df$hdr_membership, levels = scales::percent_format(accuracy = 1)(c(1, probs)))
df$hdr_membership <- NULL
}
df
}
#' @rdname geom_hdr
#' @export
geom_hdr <- function(mapping = NULL, data = NULL,
stat = "hdr", position = "identity",
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE) {
layer(
data = data,
mapping = mapping,
stat = stat,
geom = GeomHdr,
position = position,
show.legend = show.legend,
inherit.aes = inherit.aes,
params = list(
na.rm = na.rm,
...
)
)
}
#' @rdname geom_hdr
#' @format NULL
#' @usage NULL
#' @export
GeomHdr <- ggproto("GeomHdr", GeomPolygon)Package development – unit testing
James Otto (Baylor University)