Function used to specify univariate histogram density estimator
for get_hdr_1d() and layer functions (e.g. geom_hdr_rug()).
Details
For more details on the use and implementation of the method_*_1d() functions,
see vignette("method", "ggdensity").
Examples
# Histogram estimators can be useful when data has boundary constraints
df <- data.frame(x = rexp(1e3))
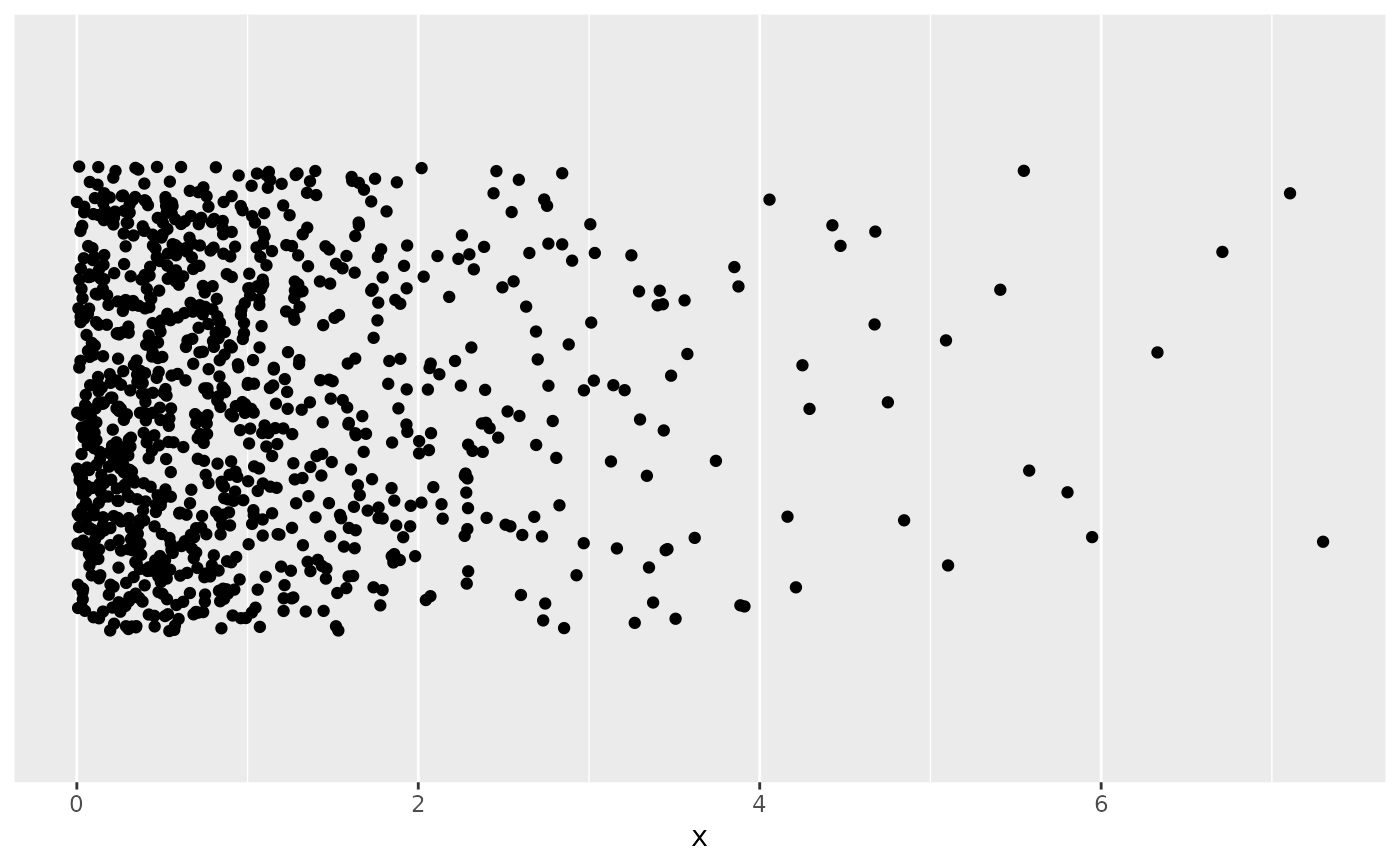
# Strip chart to visualize 1-d data
p <- ggplot(df, aes(x)) +
geom_jitter(aes(y = 0), width = 0, height = 2) +
scale_y_continuous(name = NULL, breaks = NULL) +
coord_cartesian(ylim = c(-3, 3))
p
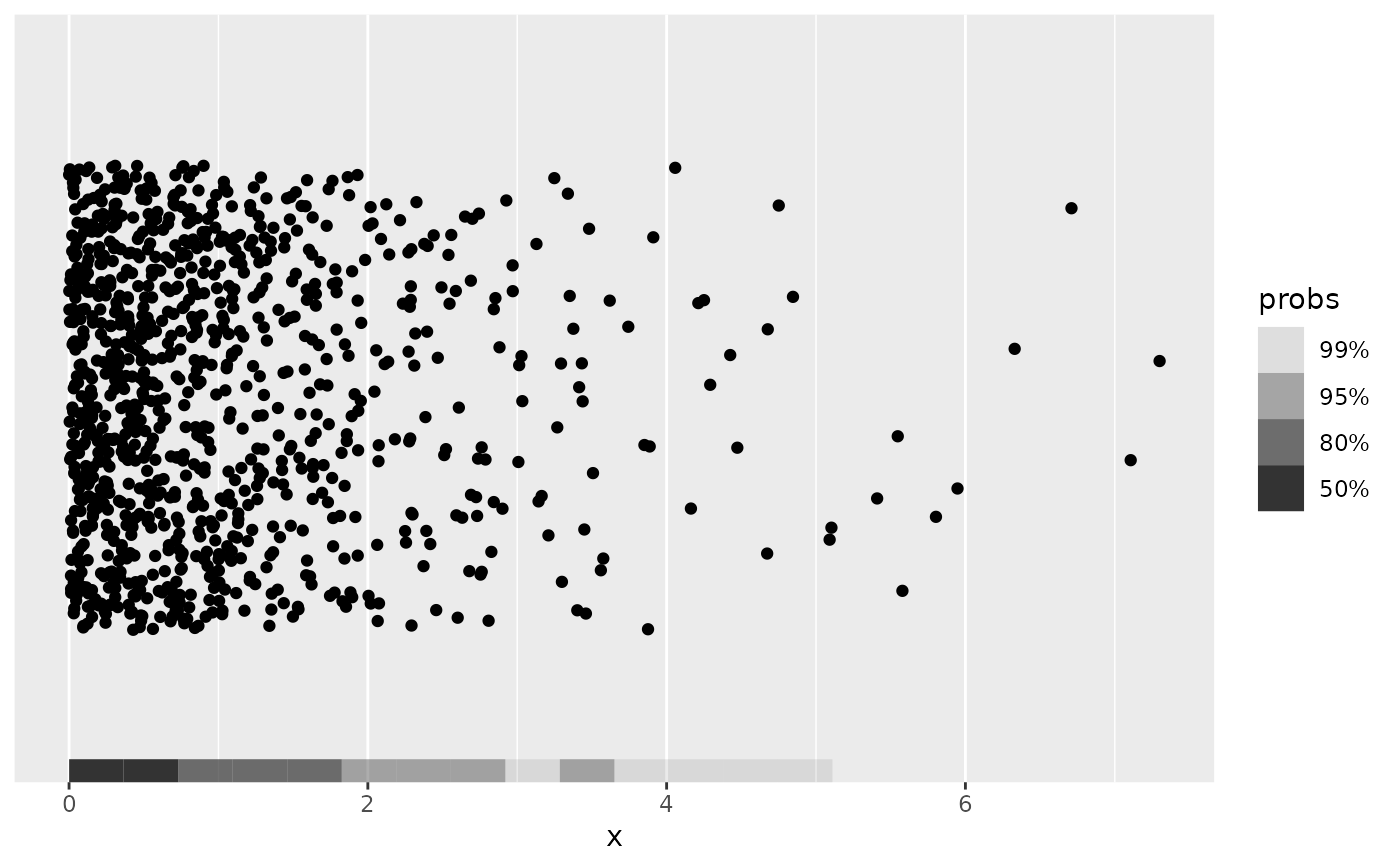
 p + geom_hdr_rug(method = method_histogram_1d())
p + geom_hdr_rug(method = method_histogram_1d())
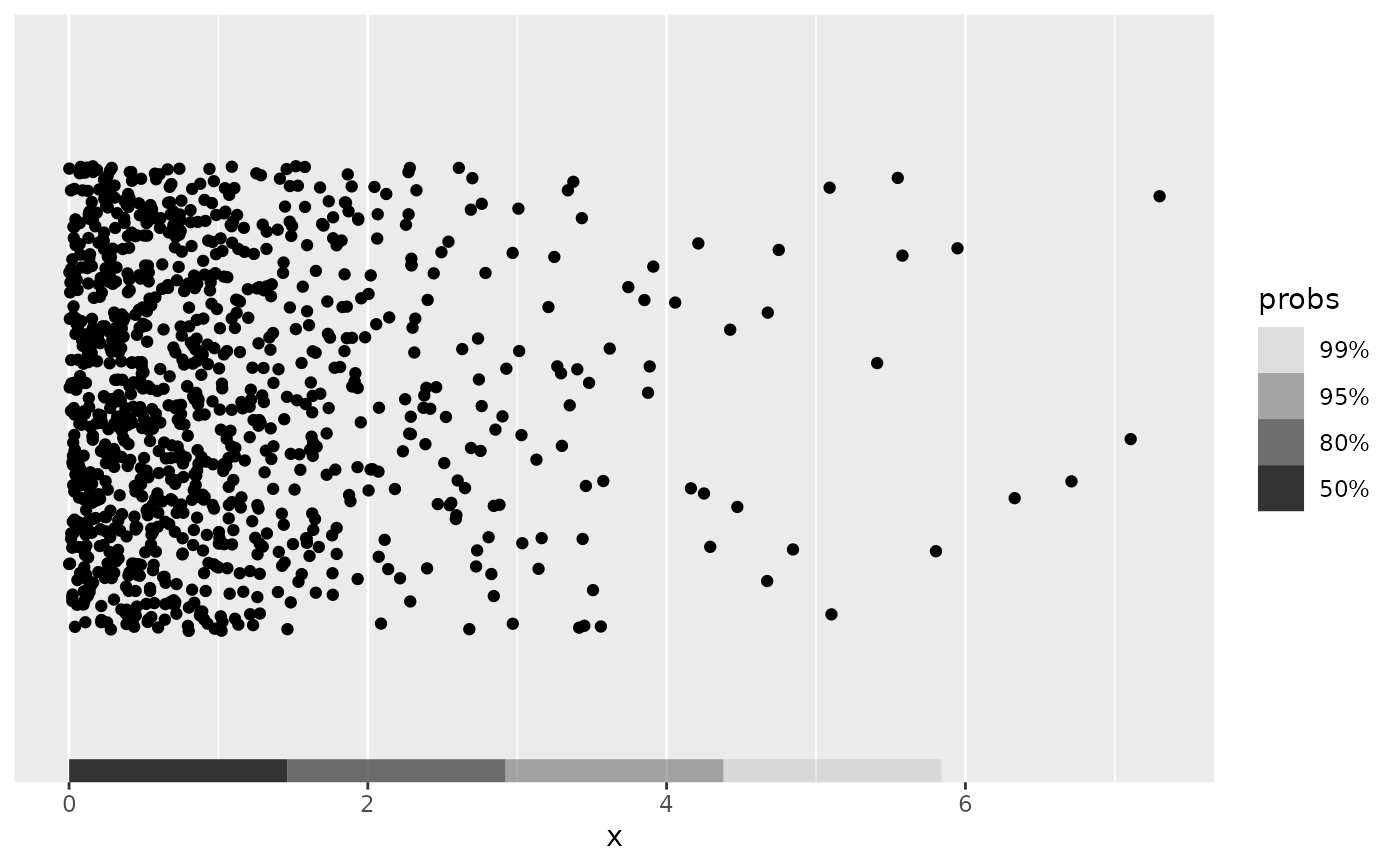
 # The resolution of the histogram estimator can be set via `bins`
p + geom_hdr_rug(method = method_histogram_1d(bins = 5))
# The resolution of the histogram estimator can be set via `bins`
p + geom_hdr_rug(method = method_histogram_1d(bins = 5))
 # Can also be used with `get_hdr_1d()` for numerical summary of HDRs
res <- get_hdr_1d(df$x, method = method_histogram_1d())
str(res)
#> List of 3
#> $ df_est:'data.frame': 20 obs. of 4 variables:
#> ..$ x : num [1:20] 0.183 0.548 0.913 1.278 1.643 ...
#> ..$ fhat : num [1:20] 0.3023 0.2132 0.1682 0.0911 0.0681 ...
#> ..$ fhat_discretized: num [1:20] 0.3023 0.2132 0.1682 0.0911 0.0681 ...
#> ..$ hdr : num [1:20] 0.5 0.5 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.95 0.95 0.95 0.99 0.95 ...
#> $ breaks: Named num [1:5] 0.004 0.017 0.0681 0.2132 Inf
#> ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:5] "99%" "95%" "80%" "50%" ...
#> $ data :'data.frame': 1000 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x : num [1:1000] 0.224 0.633 0.343 0.385 2.754 ...
#> ..$ hdr_membership: num [1:1000] 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.95 0.5 0.5 0.95 0.99 0.5 ...
# Can also be used with `get_hdr_1d()` for numerical summary of HDRs
res <- get_hdr_1d(df$x, method = method_histogram_1d())
str(res)
#> List of 3
#> $ df_est:'data.frame': 20 obs. of 4 variables:
#> ..$ x : num [1:20] 0.183 0.548 0.913 1.278 1.643 ...
#> ..$ fhat : num [1:20] 0.3023 0.2132 0.1682 0.0911 0.0681 ...
#> ..$ fhat_discretized: num [1:20] 0.3023 0.2132 0.1682 0.0911 0.0681 ...
#> ..$ hdr : num [1:20] 0.5 0.5 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.95 0.95 0.95 0.99 0.95 ...
#> $ breaks: Named num [1:5] 0.004 0.017 0.0681 0.2132 Inf
#> ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:5] "99%" "95%" "80%" "50%" ...
#> $ data :'data.frame': 1000 obs. of 2 variables:
#> ..$ x : num [1:1000] 0.224 0.633 0.343 0.385 2.754 ...
#> ..$ hdr_membership: num [1:1000] 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.95 0.5 0.5 0.95 0.99 0.5 ...